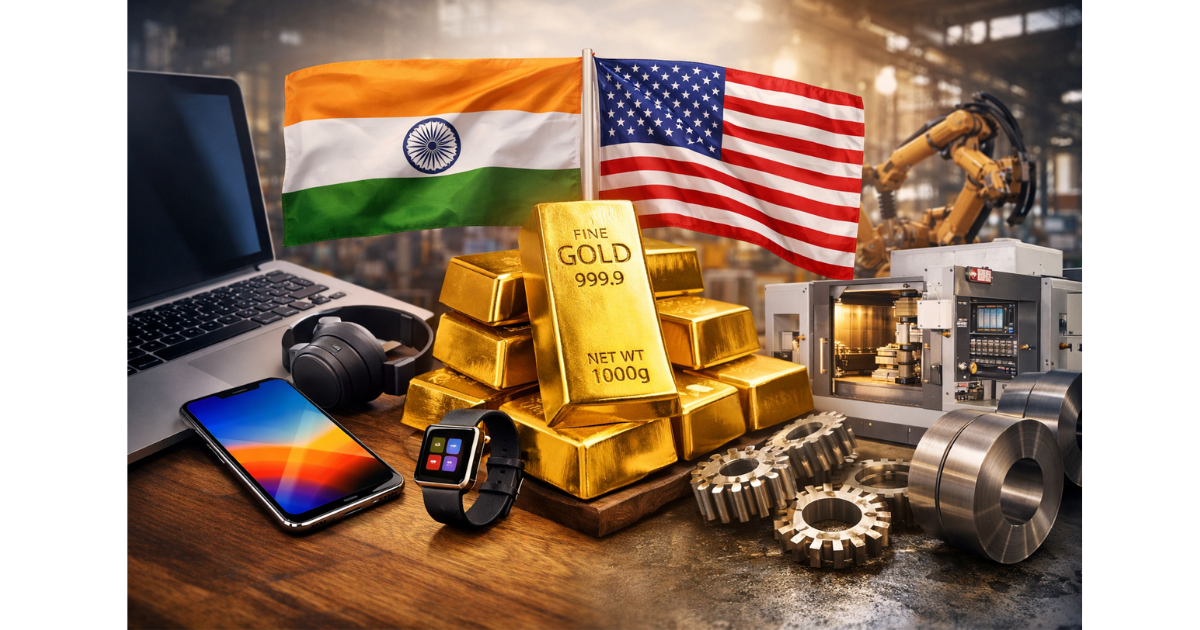
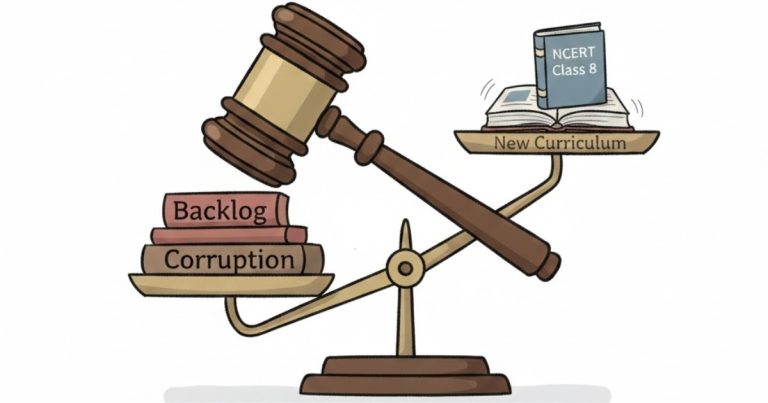
The India-US trade agreement is influencing the prices of electronics, gold, and key industrial goods in India by reducing trade barriers and improving supply chain efficiency.
The evolving India-US trade agreement is increasingly shaping the price landscape of everyday and high-value goods in the Indian market. As both countries work toward deeper economic cooperation, the impact is being felt not just in export numbers or diplomatic statements, but directly in the prices consumers pay for electronics, precious metals like gold, and critical industrial inputs. The agreement reflects a strategic alignment between two major economies and carries significant implications for inflation, manufacturing competitiveness, and household spending in India.
Strengthening Trade Ties Between Two Major Economies
India and the United States share one of the world’s fastest-growing bilateral trade relationships, spanning technology, defence, energy, and manufacturing. Recent trade negotiations have focused on reducing tariff barriers, simplifying customs procedures, and improving market access for key sectors. While the agreement stops short of a full free trade pact, it includes targeted concessions that influence pricing mechanisms across multiple industries.
For India, the trade arrangement is part of a broader effort to integrate with global supply chains while protecting domestic manufacturing. For the United States, it offers access to one of the world’s largest consumer markets and a strategic partner in Asia. These objectives converge most visibly in sectors such as electronics, gold trade channels, and industrial goods.
Electronics Become More Affordable for Consumers
One of the most immediate effects of the India-US trade agreement is seen in the electronics sector. Reduced import duties on select electronic components, semiconductors, and high-end devices sourced from the US have contributed to cost moderation. This has particular relevance for smartphones, laptops, networking equipment, and advanced medical electronics that rely on US technology or components.
Lower tariffs and streamlined customs clearance reduce input costs for Indian manufacturers assembling devices domestically under the Make in India initiative. As production costs ease, companies are better positioned to offer competitive pricing to consumers or invest in improved features without significantly raising prices. Over time, this has helped slow price inflation in premium electronics, even as global supply chains face pressure from geopolitical uncertainties.
At the same time, the agreement encourages US companies to expand manufacturing and sourcing partnerships in India, which further stabilises prices by reducing dependency on distant supply routes.
Impact on Gold Prices and Import Dynamics
Gold, a culturally and economically significant commodity in India, is also indirectly influenced by trade arrangements with the United States. While gold pricing is largely determined by global markets and currency movements, trade facilitation measures play a role in shaping import costs.
The agreement has improved financial cooperation and transparency in bullion trade channels, particularly for institutional and investment-grade gold imports routed through international markets where US financial institutions have a strong presence. Reduced transaction costs, better access to hedging instruments, and smoother compliance norms help Indian importers manage price volatility more effectively.
Although customs duties on gold remain a policy lever for the Indian government to manage trade deficits, efficiency gains through international trade cooperation can marginally soften landed costs. For consumers, this does not always translate into immediate price drops, but it contributes to more stable pricing during periods of global uncertainty.
Industrial Goods and Manufacturing Inputs See Cost Rationalisation
The most strategic impact of the India-US trade agreement is visible in industrial goods and manufacturing inputs. Reduced tariffs on specialised machinery, aerospace components, industrial chemicals, and advanced engineering equipment from the US have lowered capital costs for Indian industries.
Sectors such as renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, automotive manufacturing, and heavy engineering benefit directly from access to high-quality US equipment at more competitive prices. This improves productivity, enhances export competitiveness, and reduces the overall cost of production. Over time, these savings can trickle down into lower prices for finished goods, from automobiles to consumer appliances.
For small and medium enterprises, easier access to imported industrial inputs helps bridge technology gaps and supports integration into global value chains, a long-term objective of India’s industrial policy.
Currency Stability and Inflation Management
Beyond tariffs, the trade agreement also contributes to macroeconomic stability. Increased trade volumes with the United States strengthen foreign exchange inflows and support the rupee during periods of global volatility. A relatively stable currency helps contain imported inflation, especially for dollar-denominated goods such as electronics and industrial machinery.
This indirect effect is particularly important at a time when global inflationary pressures and supply disruptions continue to affect commodity prices worldwide.
What It Means for Indian Consumers and Businesses
For Indian consumers, the agreement offers gradual relief rather than dramatic price cuts. Electronics may become more affordable or feature-rich at the same price point, while gold prices benefit from improved stability rather than sharp declines. For businesses, especially manufacturers, the agreement lowers operational costs and encourages investment in modern technology.
The broader significance lies in predictability. Trade agreements create a stable policy environment, allowing companies to plan pricing, sourcing, and expansion strategies with greater confidence.
A Long-Term Shift in India’s Trade Landscape
The India-US trade agreement marks a steady shift toward deeper economic integration with global partners while balancing domestic priorities. Its impact on the cost of electronics, gold, and industrial goods illustrates how trade policy decisions influence everyday economic realities.
As negotiations continue and cooperation expands into new areas such as digital trade and clean energy, the price effects are likely to become more pronounced. For now, the agreement serves as a reminder that international diplomacy increasingly shapes what Indian consumers pay at the checkout counter and how competitive Indian industries remain on the global stage.
Add newsvent.in as a preferred source on google – click here
Last Updated on: Wednesday, February 4, 2026 6:20 pm by News Vent Team | Published by: News Vent Team on Wednesday, February 4, 2026 11:57 am | News Categories: News